Java is a high-level programming language originally developed by Sun Microsystems and released in 1995. Java runs on a variety of platforms, such as Windows, Mac OS, and the various versions of UNIX. This tutorial gives a complete understanding of Java. This reference will take you through simple and practical approaches while learning Java Programming language.

Why to Learn java Programming?
Java is a MUST for students and working professionals to become a great Software Engineer specially when they are working in Software Development Domain. I will list down some of the key advantages of learning Java Programming:
Object Oriented − In Java, everything is an Object. Java can be easily extended since it is based on the Object model.
Platform Independent − Unlike many other programming languages including C and C++, when Java is compiled, it is not compiled into platform specific machine, rather into platform independent byte code. This byte code is distributed over the web and interpreted by the Virtual Machine (JVM) on whichever platform it is being run on.
Simple − Java is designed to be easy to learn. If you understand the basic concept of OOP Java, it would be easy to master.
Secure − With Java's secure feature it enables to develop virus-free, tamper-free systems. Authentication techniques are based on public-key encryption.
Architecture-neutral − Java compiler generates an architecture-neutral object file format, which makes the compiled code executable on many processors, with the presence of Java runtime system.
Portable − Being architecture-neutral and having no implementation dependent aspects of the specification makes Java portable. Compiler in Java is written in ANSI C with a clean portability boundary, which is a POSIX subset.
Robust − Java makes an effort to eliminate error prone situations by emphasizing mainly on compile time error checking and runtime checking.
Sun has defined and supports four editions of Java targeting different application environments and segmented many of its APIs so that they belong to one of the platforms. The platforms are:
- Java Card for smart-cards.
- Java Platform, Micro Edition (Java ME) – targeting environments with limited resources.
- Java Platform, Standard Edition (Java SE) – targeting workstation environments.
- Java Platform, Enterprise Edition (Java EE) – targeting large distributed enterprise or Internet environments.
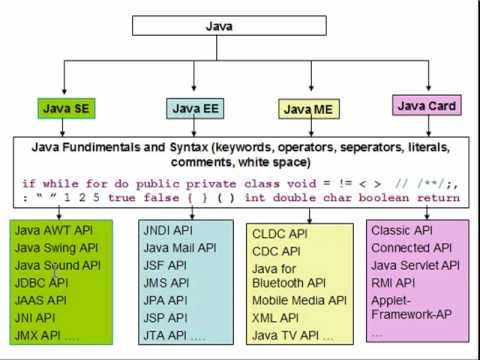
Java Editions
Hello World using Java Programming.
Just to give you a little excitement about Java programming, I'm going to give you a small conventional C Programming Hello World program, You can try it using Demo link.
public class First_program { public static void main(String []args) { System.out.println("Hello World"); // prints Hello World } }

Comments
Post a Comment